Servers
The web pages that we interact with in our day-to-day life are built using only three technologies: HTML, CSS and JavaScript.
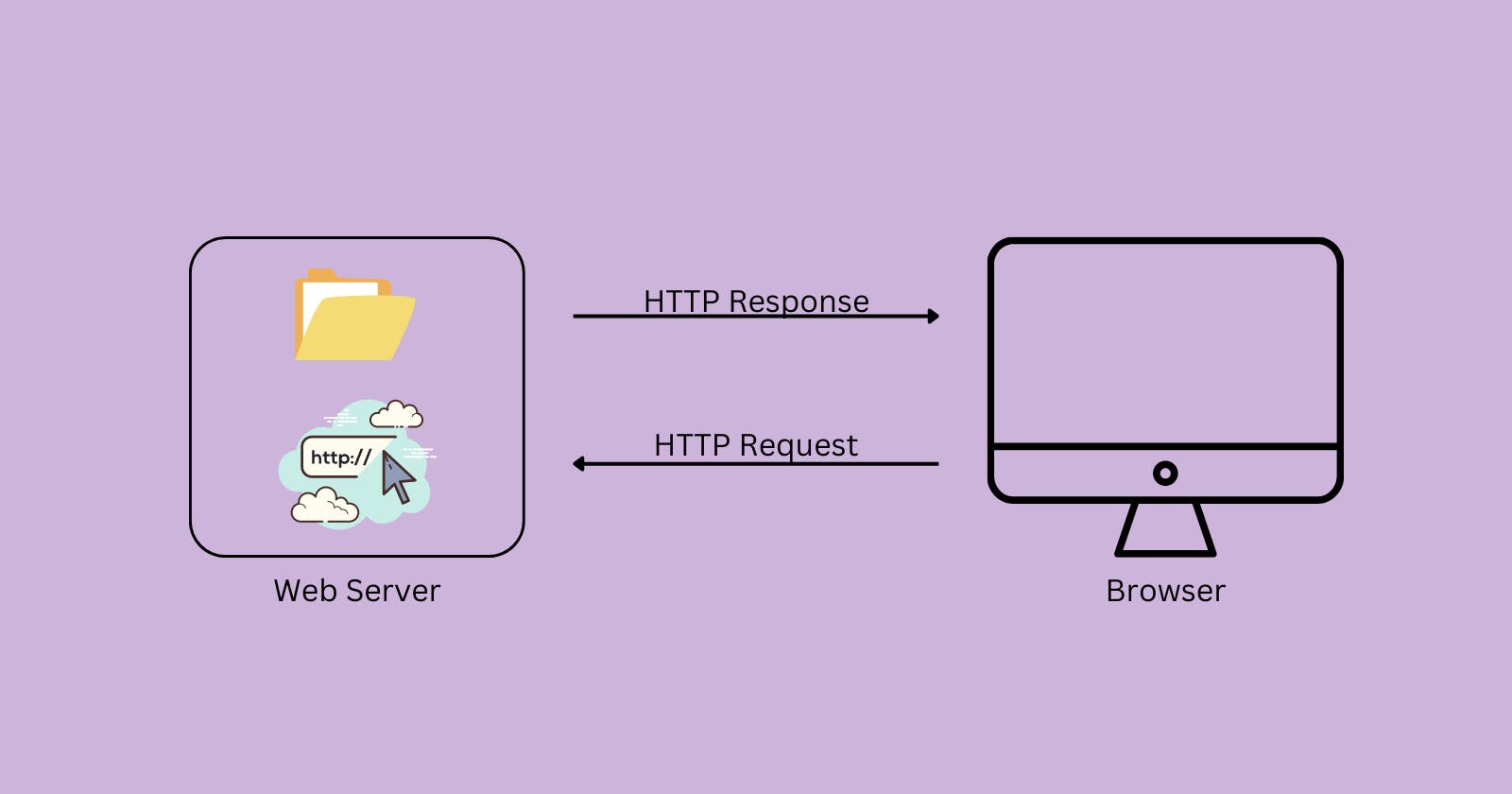
These pages are created in our local environment, which is a local host, but then they must be published online so that anybody on the internet can access them. This web page can be published on the internet with the help of a web server.
What is a web server?
As the name suggests, a web server is a software program that stores all the web page files, such as HTML, CSS and many more, on a computer running Linux as its operating system and delivers all this information to the browser when it is requested.
Apache
Apache HTTP Server delivers web content via the Internet as a free and open source application. In a short period of time, the HTTP client became the most popular on the web and was commonly known as Apache.
Live Server
A web page is constantly changing, so every time we make a change, we need to reload the webpage to see the changes. Ritwick Dey solved this problem by developing Live Server extension that reloads it automatically and saves development time.
He monitors the files and loads them again if they are changed. When we launch the live server, the script he wrote for this tracking is incorporated in our code.
<!-- Code injected by live-server -->
<script>
// <![CDATA[ <-- For SVG support
if ('WebSocket' in window) {
(function () {
function refreshCSS() {
var sheets = [].slice.call(document.getElementsByTagName("link"));
var head = document.getElementsByTagName("head")[0];
for (var i = 0; i < sheets.length; ++i) {
var elem = sheets[i];
var parent = elem.parentElement || head;
parent.removeChild(elem);
var rel = elem.rel;
if (elem.href && typeof rel != "string" || rel.length == 0 || rel.toLowerCase() == "stylesheet") {
var url = elem.href.replace(/(&|\?)_cacheOverride=\d+/, '');
elem.href = url + (url.indexOf('?') >= 0 ? '&' : '?') + '_cacheOverride=' + (new Date().valueOf());
}
parent.appendChild(elem);
}
}
var protocol = window.location.protocol === 'http:' ? 'ws://' : 'wss://';
var address = protocol + window.location.host + window.location.pathname + '/ws';
var socket = new WebSocket(address);
socket.onmessage = function (msg) {
if (msg.data == 'reload') window.location.reload();
else if (msg.data == 'refreshcss') refreshCSS();
};
if (sessionStorage && !sessionStorage.getItem('IsThisFirstTime_Log_From_LiveServer')) {
console.log('Live reload enabled.');
sessionStorage.setItem('IsThisFirstTime_Log_From_LiveServer', true);
}
})();
}
else {
console.error('Upgrade your browser. This Browser is NOT supported WebSocket for Live-Reloading.');
}
// ]]>
</script>
HTML
HTML, often known as Hyper Text Markup Language, is a markup language used for creating websites and web applications. A web application's skeleton is built using HTML to build a structure for web documents.
A HTML file should be saved with either .html or.htm extension, and it should be named index.html or default.html in accordance with coding conventions.
What is HTML5 ?
The most recent and comprehensive version of HTML, known as HTML5, added numerous significant updates and brand-new capabilities, including multimedia support, enhanced document markup, APIs, etc.
New elements in HTML5 include <video>, <main>, <article>, etc. Along with the aforementioned capabilities, HTML5's syntax was changed and is now based on Document Type Declaration.
What is Tag?
In essence, an HTML tag allows the browser to differentiate between a document, an element, and regular content. A tag is always enclosed in two angle brackets, like this <>...</> lets take example of paragraph tag.
<p>Hi Everyone</p>
What is Element?
Everything between the initial tag and the closing/ending tag is referred to as an HTML element. Below is a fantastic illustration of an HTML element.
<StartingTag> The content to display </EndingTag>
Some elements, such as the <img> tag, lack a closing or ending tag.
What is Attribute?
In HTML, an attribute is used to specify additional tag-related information. For instance, a style attribute can be used to add additional content to a <h1> tag if we wish to style that particular tag.
Structure of HTML
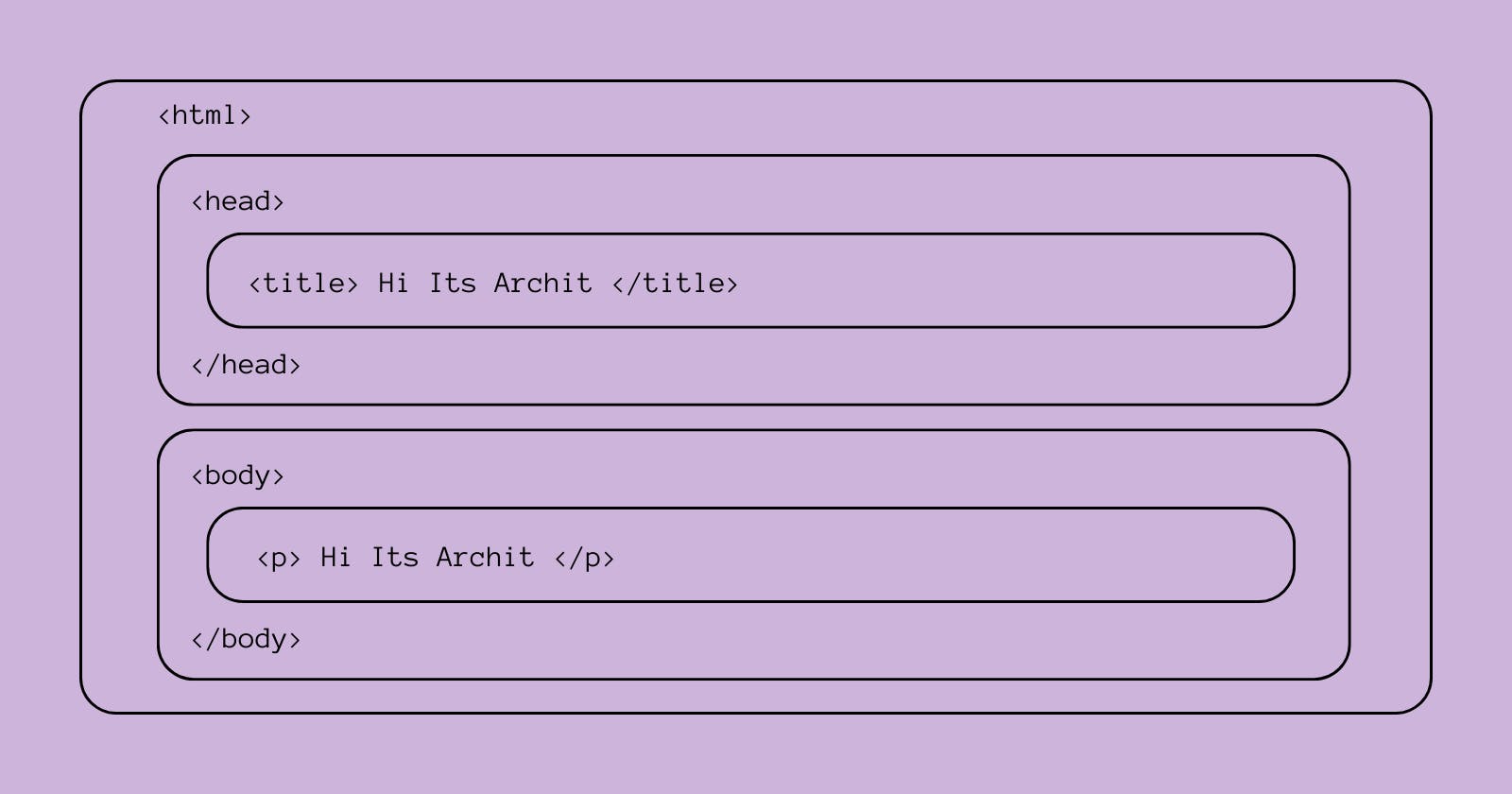
The image above demonstrates the HTML structure, where everything in the <head> tag is displayed to the browser and everything in the <body> tag is displayed to viewers as part of the web page.
Lets take the example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello</h1>
</body>
</html>
Standard HTML Tags
<!DOCTYPE html>
The DOCTYPE declaration informs the web browser of the HTML version used to create the page. This guarantees that the web page is parsed uniformly across web browsers.
<html>
This is the opening HTML tag, often known as the root or parent tag.
<head>
All of the meta data for the document is contained in this tag. While loading, these details are hidden from end users.
<title>
An HTML document's title is specified by this tag.
<body>
This tag basically defines the body structure of an HTML document and contains all the main content of a website.
Essential Tags for Your HTML Document
Paragraph Tag
The <p> tag is used to create a paragraph in an HTML document.
Example:-
<p>Enter Paragraph Here...</p>
Output:-
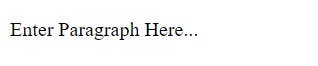
Heading Tag
For writing a Heading in HTML we use different types of tag ranging from <h1> to <h6>
Example:-
<h1>Enter Main Heading Here...</h1>
<h2>Enter Secondary Heading Here...</h2>
Output:-

Anchor Tag
A hyperlink, which is used to connect pages, is defined by the <a> element. Href is basically the URL that the hyperlink points to.
Example:-
<a href="where to navigate">Enter Link Name Here...</a>
Output:-

Line Break Tag
A line break in text is produced by the HTML element <br>. It is helpful when composing a poem or an address where the line breaks matter.
Example:-
<p>I m on line one <br> I m on line two</p>
Output:-
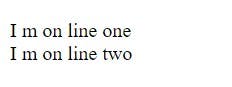
Image Tag
The HTML <img> tag is used to show or embed images in web pages.
Attributes:
src: This attribute is required, and it also contains the URL or path of the image to displayalt: Defines an alternative text description of the image, It is useful if image is having some issues than this text is displayed.loading: Indicates how the browser should load the image. There are two types of loading, firsteagerwhich loads immediately and secondlazywhich loads image when it comes under a particular viewport
So, that concludes our discussion on HTML and web servers. Thank you so much if you made it this far; I'd love to hear your thoughts.